
Traditionally, we’ve focused our fitness efforts on physical factors like diet, exercise type, and intensity to achieve our workout goals. However, we often overlook a critical element that can significantly enhance our performance: sound frequencies.
Music and sound are integral parts of our daily lives, from waking up to an alarm clock, listening to the radio on our commute, to the beat that carries us through our workout session. But have you ever stopped to consider how sound, more specifically sound frequencies, might be affecting your exercise routine? Sound frequencies, the speed of sound vibrations which determines the pitch we hear, have a profound impact on our bodies and minds, whether we realize it or not. It can affect our mood, focus, and even physical performance.
Contents
Introduction to Sound Frequencies and Fitness
Whether you’re a seasoned athlete or someone who’s just embarking on a fitness journey, you’ve probably already discovered the energizing role that music can play in your workout routine. However, the impact of sound on our exercise performance goes beyond simply having a good beat to move to. In particular, the frequencies of the sounds we listen to can significantly influence how we exercise, affecting everything from our rhythm and pace to our focus and motivation.
Definition of Sound Frequencies
Sound frequencies refer to the number of sound waves that pass a certain point in a given period of time. They’re measured in Hertz (Hz), and higher frequencies correspond to higher-pitched sounds. To put it simply, if you think about music, a bass guitar produces low-frequency sounds, while a flute produces high-frequency sounds. It’s this variation in frequencies that gives music its richness and depth.
The Role of Music in General Fitness
Music has always had a deep-rooted connection with fitness and exercise. It helps set the pace of our workouts, keeps us motivated, and makes the overall experience more enjoyable. Various studies have shown that listening to music while exercising can increase endurance, elevate mood, and even reduce the perception of effort. While all these benefits are substantial, they mostly relate to the rhythm and tempo of the music. The concept of sound frequencies takes this a step further, suggesting that the pitch of the sounds we listen to could have a direct impact on our physical performance.
Brief Overview of the Impact of Sound Frequencies on Workout Performance
Over the years, researchers have delved into the world of sound frequencies and their influence on human performance. They’ve found that certain frequencies can enhance concentration, improve body movement and coordination, and even boost stamina during workouts. For instance, lower frequencies (below 300 Hz) are often associated with a calming and relaxing effect, potentially beneficial for exercises like yoga. In contrast, higher frequencies (above 2,000 Hz) can stimulate and energize, which might help in high-intensity workouts.
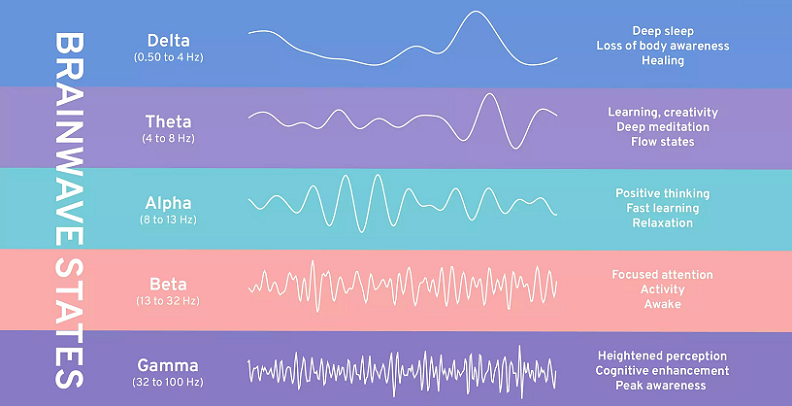
Understanding the Science of Sound Frequencies
To fully appreciate the role of sound frequencies in enhancing workout performance, it’s important to understand the underlying science. This involves a basic understanding of what sound frequencies are and how they work, how the human body responds to different frequencies, and an overview of the scientific research that supports these concepts.
Sound Frequency Basics: What They Are and How They Work
As mentioned earlier, sound frequencies refer to the number of sound waves passing a specific point in a set period. This frequency determines the pitch of the sound: higher frequencies result in higher-pitched sounds, and lower frequencies in lower-pitched sounds. Sound frequencies are measured in units called Hertz (Hz). For instance, a sound wave that completes 500 cycles per second is said to have a frequency of 500 Hz [1].
Sound waves are transmitted through the air and other media to our ears, which translate these waves into signals that our brains can understand. This is the fundamental principle of how we hear and interpret sound. However, the frequency of these sounds doesn’t just influence the pitch we perceive; it can also affect our physical and emotional states.
The Human Body’s Response to Different Sound Frequencies
The human body is an incredible machine, capable of responding to the environment in a myriad of ways. Just as our bodies react to the sight of a beautiful sunset or the smell of our favorite food, they also respond to different sound frequencies.
Lower frequencies (below 300 Hz) can slow down our brainwaves and are often associated with calming, soothing effects. These frequencies can encourage a meditative state and may enhance workouts focused on flexibility, balance, and mindfulness, like yoga or Tai Chi.
Mid-range frequencies (300 Hz to 2,000 Hz) typically promote a relaxed alertness and can be particularly effective for steady-state, moderate-intensity exercises such as jogging or cycling.
Higher frequencies (above 2,000 Hz) can stimulate brain activity and energize the listener. These frequencies are often used in high-intensity workouts, encouraging power, strength, and speed [2].
Overview of Scientific Studies on Sound Frequencies and Physical Performance
Multiple studies over the years have examined the effects of sound frequencies on physical performance. A study published in the Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology found that synchronizing movements with music enables athletes to perform more efficiently, indicating the potential power of sound frequencies.
Another study in the journal Scientific Reports revealed that specific sonic frequencies could enhance the effect of music-driven rhythmic auditory cueing in movement therapies, suggesting that sound frequencies could be used to boost motor performance.
Though more research is needed to establish direct, universally-applicable relationships between specific sound frequencies and specific exercise types, the initial findings are indeed promising [3].

Impact of Different Sound Frequencies on Workout Performance
Having grasped the science behind sound frequencies, it’s now time to delve into how these frequencies can impact workout performance. Each range of frequencies, from low to high, influences the body differently and can thus cater to different types of workouts. By understanding the effects of these frequencies, you can tailor your workout soundtrack to match your exercise regimen, helping you achieve better results.
The Effects of Low-Frequency Sounds on Workout Performance
Low-frequency sounds, typically below 300 Hz, are recognized for their soothing and calming effects. But how does this translate into a workout setting?
These frequencies can help to create a relaxed state of mind, which is essential for exercises that require calm, focus, and deep concentration. When performing yoga, pilates, or Tai Chi, for instance, low-frequency music can aid in achieving a meditative state. It can help you focus on your breathing, reduce stress levels, and improve your body’s flexibility and balance.
Moreover, a study published in the American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation suggests that listening to low-frequency music can alleviate pain during and after strenuous exercises. This can make it a beneficial addition to post-workout recovery routines [4].
The Effects of Mid-Frequency Sounds on Workout Performance
Mid-frequency sounds, usually ranging from 300 Hz to 2,000 Hz, strike a balance between calming and energizing effects. These sounds promote a state of relaxed alertness, making them a great match for moderate-intensity exercises.
Whether you’re cycling, hiking, or performing a light cardio session, mid-frequency sounds can enhance your overall performance. They can help maintain a steady rhythm, which is particularly beneficial when you’re aiming for consistent pacing in your workout. Plus, these sounds can stimulate a positive mood, making your workout experience more enjoyable [5].
The Effects of High-Frequency Sounds on Workout Performance
High-frequency sounds, typically above 2,000 Hz, are known for their stimulating and energizing effects. These sounds can wake up your brain, increase alertness, and pump up your adrenaline levels.
If you’re engaging in high-intensity interval training (HIIT), weightlifting, or fast-paced sports like basketball or soccer, high-frequency sounds can be your perfect workout companion. They can boost your performance, helping you push your limits, increase your speed, and enhance your power output. Furthermore, these sounds can make strenuous workouts feel less exhausting by providing a distraction and lifting your spirits [6].

Practical Applications: Using Sound Frequencies to Enhance Your Workout
Now that we’ve explored the science behind sound frequencies and their effects on workout performance, let’s translate this knowledge into action.
How to Choose Music with the Right Sound Frequencies for Your Workout
The key to enhancing your workout with sound frequencies is to match the frequency range with the intensity and nature of your exercise. You can use tools like audio frequency analyzers, available online or as mobile apps, to identify the dominant frequencies in your favorite tracks [7].
For lower intensity workouts that require a calm state of mind, such as yoga or meditation, opt for music with a dominance of lower frequencies. This might be slow-tempo music, ambient sounds, or nature sounds like ocean waves.
If you’re doing moderate-intensity exercises like jogging or cycling, go for music that has a balance of mid-range frequencies. This could be pop music or light rock, which often carry these frequencies.
For high-intensity workouts such as HIIT or weightlifting, choose music with high-frequency sounds. Upbeat dance music, heavy metal, or fast-paced electronic music can be good choices for these kinds of workouts.
Remember, the idea isn’t to restrict your musical choices but to guide you in creating a workout playlist that will optimize your performance.
Examples of Workout Genres and Their Suitable Sound Frequencies
Let’s look at some examples of different workout genres and the suitable sound frequencies for each:
- Yoga and Mindfulness Exercises: These workouts benefit from lower sound frequencies. Consider slow-tempo classical music, ambient sounds, or even the calming sounds of a rainforest or flowing water.
- Steady-state Cardio: Mid-frequency sounds complement these workouts well. Genres like pop, light rock, or easy-listening electronic music would be great choices.
- High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT): High-frequency sounds are excellent for boosting the intensity of these workouts. You could consider genres like EDM, techno, or heavy metal.
Case Studies: Successful Application of Sound Frequencies in Workout Regimens
There are numerous cases where applying the principles of sound frequencies has positively impacted workout performance. For instance, professional trainers and athletes often curate their workout playlists to align with the intensity of their training.
Take the example of Eliud Kipchoge, the world record holder for the men’s marathon. In an interview, he shared that he listens to mid-to-high frequency music while training, believing it helps him maintain his pace and focus.
In another instance, the British Olympic Synchronized Swimming Team used a mix of music with different sound frequencies to aid their training routines, helping them synchronize their movements in the water.
The Role of Sound Frequencies in Specific Types of Exercise
Understanding the broad impact of sound frequencies on workout performance is beneficial, but it’s equally important to recognize how they can enhance specific types of exercises.
Sound Frequencies and Cardiovascular Workouts
Cardiovascular exercises, such as running, cycling, and swimming, are typically rhythm-based, and the tempo of the music can help maintain a steady pace. But beyond the tempo, the frequencies of the music play a crucial role too.
Mid-range frequencies are typically well-suited for steady-state cardio workouts. They provide a balanced sound profile that maintains alertness without over-stimulating the listener. Songs that fall into the pop, light rock, or electronic genres often fit this frequency range.
However, if you’re pushing for a higher-intensity cardio workout, such as a sprint session, high-frequency sounds can help increase your energy levels and stimulate faster movement.
Sound Frequencies and Strength Training Workouts
Strength training involves shorter, more intense bouts of exercise, whether that’s lifting weights, performing bodyweight exercises, or using resistance equipment. During these workouts, the energizing impact of high-frequency sounds can prove beneficial.
Upbeat, fast-paced music with high frequencies can help elevate the heart rate, stimulate the nervous system, and consequently improve performance during high-intensity exercises. Music genres like heavy metal, upbeat electronic, or high-energy rock could serve as ideal accompaniments for your strength training sessions.
Sound Frequencies and Yoga or Mindfulness Exercises
Unlike cardio and strength training, yoga and mindfulness exercises focus on calming the mind, enhancing flexibility, and improving balance. These exercises thrive on the relaxing effects of low-frequency sounds.
Music and sounds with dominant low frequencies, such as ambient music, classical tracks, or nature sounds (like a babbling brook or gentle rain), can aid in achieving a meditative state. These frequencies can slow down brainwaves, helping you focus inward, regulate your breathing, and fully engage in each yoga pose or mindfulness activity.
References
[1] The Science Behind Binaural Beats for Exercise Intensity
[2] How Athletes Are Using Sound Therapy to Get Race Ready
[3] Musical Intensity Applied in the Sports and Exercise Domain: An Effective Strategy to Boost Performance?
[4] 40-Hz Binaural beats enhance training
[5] Let’s Get Physical: The Psychology of Effective Workout Music
[6] Listening to 15 Hz Binaural Beats Enhances the Connectivity of Functional Brain Networks
[7] Can Listening to Music Improve Your Workout?





