
Mangosteen, a fruit native to Southeast Asia, has not only captivated taste buds around the globe with its sweet and tangy flavor but has also piqued the interest of health enthusiasts and researchers alike. In traditional medicine, mangosteen has been cherished for centuries. But what makes it relevant in modern-day health and wellness is its potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Contents
Introduction to Mangosteen
Mangosteen, a gem from the tropics, is known for its delectable sweet-sour taste and has captured the attention of both health aficionados and scientific researchers. With a history steeped in traditional medicine where it has been valued for hundreds of years, mangosteen offers a rich array of nutrients.
Background Information on Mangosteen
Before we delve into the health benefits of mangosteen, let’s take a moment to understand what this fruit is and where it comes from. Its intriguing history reveals why it has been so valued in various cultures for its medicinal properties.
Definition and Origin of Mangosteen
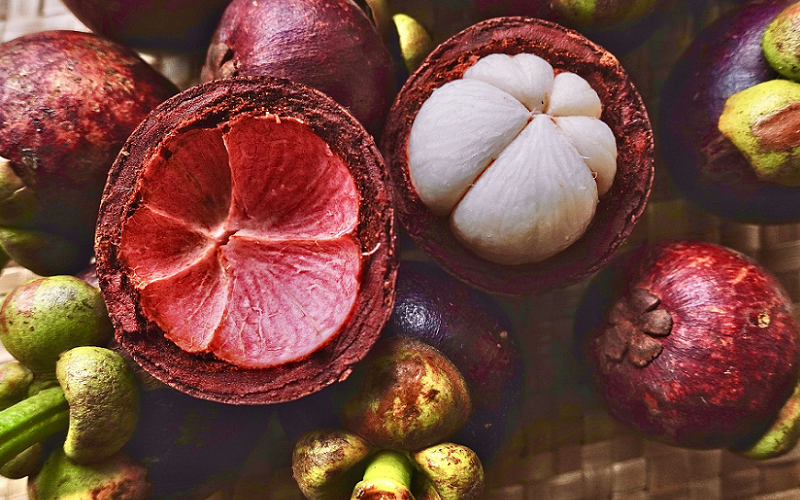
Mangosteen, scientifically known as Garcinia mangostana, is a small, round fruit with a deep purple rind and juicy white flesh. Native to the Sunda Islands and the Moluccas of Indonesia, mangosteen has been cultivated in the tropical regions of Southeast Asia for centuries. The fruit is roughly the size of a tangerine and has a thick, leathery rind that encases delicate, segmented flesh. It is prized for its uniquely sweet and slightly acidic flavor.
Historical Uses in Traditional Medicine
The use of mangosteen in traditional medicine dates back hundreds of years. In Southeast Asia, the fruit and its various parts, including the rind and leaves, have been used to treat a plethora of ailments ranging from digestive disorders to skin infections. It has been a common ingredient in traditional Southeast Asian medicine, particularly in countries like Thailand, Malaysia, and Indonesia. The rind was often used to make tea or extracts, while the fruit itself was consumed for general health benefits.
Relevance of Mangosteen in Modern Health
Now that we’ve touched upon the origins of mangosteen and its historical significance, let’s shift our focus to the modern-day relevance of this exotic fruit. With the growing interest in natural remedies and holistic health, mangosteen is gaining recognition on a global scale.
Increasing Interest in Natural Remedies
In recent years, there has been a surge in interest in natural remedies and plant-based diets. As more people look for alternatives to pharmaceuticals and seek ways to improve their health naturally, exotic fruits like mangosteen are garnering attention for their potential medicinal properties.
Popularity in Health and Wellness Communities
Mangosteen is now widely available in various forms beyond the fresh fruit, including juices, powders, and supplements. This availability, coupled with a growing body of research into its health benefits, has led to its increasing popularity among health and wellness communities. Fitness enthusiasts, nutritionists, and individuals looking for natural health solutions are particularly interested in the potential of mangosteen to provide anti-inflammatory and antioxidant support [1].

Nutritional Profile of Mangosteen
Now that we have a good grasp of the background and relevance of mangosteen in the health community, let’s dive into the nitty-gritty of what makes this fruit a nutritional powerhouse. Understanding the nutritional profile of mangosteen is crucial in comprehending how it can be beneficial in providing anti-inflammatory and antioxidant support.
Mangosteen Main Components
Mangosteen is not just delicious; it’s also packed with essential nutrients. These nutrients are the building blocks of the numerous health benefits that mangosteen offers [2].
Vitamins
One of the prominent vitamins in mangosteen is vitamin C. Vitamin C is an essential antioxidant that supports the immune system, helps in the absorption of iron from plant-based foods, and promotes healthy skin. Besides vitamin C, mangosteen also contains small amounts of B-vitamins such as thiamin, niacin, and folate, which are essential for energy metabolism and maintaining a healthy nervous system.
Minerals
Mangosteen is also a source of several vital minerals. Potassium, a mineral essential for heart health, is present in mangosteen. Additionally, the fruit contains trace amounts of magnesium, manganese, and copper. These minerals are essential for bone health, metabolism of carbohydrates and proteins, and protection of cells from oxidative damage.
Fiber
Dietary fiber is another nutrient that mangosteen boasts. Fiber is essential for digestive health, as it aids in regular bowel movements and supports a healthy gut microbiome. Moreover, consuming fiber-rich foods like mangosteen can also be beneficial in managing weight and reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Phytochemicals and Active Compounds
Apart from the basic nutrients, mangosteen is rich in specialized compounds known as phytochemicals. These naturally occurring chemicals have potent health benefits and play a significant role in the fruit’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties [3]
Xanthones
Mangosteen is especially renowned for its high content of xanthones, a group of polyphenolic compounds. Xanthones have been studied for their powerful antioxidant properties and their potential ability to combat inflammation and cancer.
Flavonoids
Flavonoids are another group of phytochemicals found in mangosteen. Like xanthones, they have antioxidant properties, but they are also known for their potential benefits in heart health and protection against chronic diseases.
Tannins
Tannins, found in the rind of mangosteen, are polyphenolic compounds known for their astringent properties. They have been studied for their potential in reducing inflammation and combating bacterial infections.
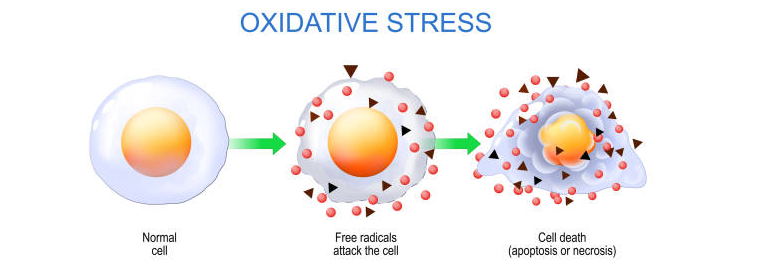
Understanding Inflammation and Oxidative Stress
Before we get into how mangosteen can help with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant support, it’s essential to understand what inflammation and oxidative stress are. These terms are often thrown around in the health and wellness community, but fully grasping their implications will help you better appreciate the benefits of incorporating mangosteen into your diet.
Definition of Inflammation
Inflammation is a biological response that occurs when your body tries to protect itself from harmful stimuli such as pathogens, irritants, or injuries. While it is generally a protective mechanism, in certain circumstances, inflammation can become detrimental.
Acute vs. Chronic Inflammation
There are two main types of inflammation – acute and chronic. Acute inflammation is short-term and occurs in response to an injury or infection. It usually resolves quickly and is characterized by redness, heat, swelling, and pain. On the other hand, chronic inflammation is a prolonged inflammatory response that can last for months or even years. Chronic inflammation can be the result of an unresolved acute inflammation, an autoimmune disorder, or long-term exposure to irritants. It is often linked to various chronic diseases like arthritis, heart disease, and diabetes [4].
The Role of Inflammation in Disease
Chronic inflammation plays a significant role in the development of various diseases. It can lead to tissue damage and contribute to the progression of conditions such as arthritis, heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative diseases. Controlling chronic inflammation is essential for preventing and managing these diseases.
Definition of Oxidative Stress
Another crucial concept to understand is oxidative stress, which is closely related to inflammation. Oxidative stress is an imbalance between the production of free radicals and the body’s ability to counteract their harmful effects through neutralization by antioxidants.
Free Radicals and Reactive Oxygen Species
Free radicals are molecules with unpaired electrons, making them highly reactive. They can cause damage to cells, proteins, and DNA. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are a type of free radicals that are oxygen-containing molecules. While ROS play essential roles in cell signaling and homeostasis, excessive levels can lead to oxidative stress and cellular damage.
Impact on Aging and Chronic Diseases
Oxidative stress has been linked to aging and various chronic diseases. It is believed to play a role in the aging process by damaging cellular components and contributing to cell death. Moreover, oxidative stress is associated with the development of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.

Anti-Inflammatory Benefits of Mangosteen
Equipped with an understanding of inflammation and its role in diseases, let’s explore how mangosteen can be a valuable ally in combating inflammation. The fruit’s unique combination of nutrients and phytochemicals provides multiple avenues through which it can exert anti-inflammatory effects [5].
How Mangosteen Reduces Inflammation
The components in mangosteen, particularly xanthones, are believed to target and modulate various pathways and molecules involved in the inflammatory process. Let’s look at how these compounds work to reduce inflammation.
Inhibition of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines
Cytokines are small proteins that play a crucial role in cell signaling during inflammatory responses. Some cytokines promote inflammation, and these are known as pro-inflammatory cytokines. Mangosteen has been found to inhibit the production of certain pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), which can help in reducing inflammation.
Modulation of Immune Response
Mangosteen also affects the immune system, which is closely linked to inflammation. It can modulate the activity of various immune cells, such as macrophages and T-cells. By regulating these cells, mangosteen can influence the immune response and subsequently the inflammatory process.
Application in Managing Chronic Inflammatory Conditions
Given its anti-inflammatory properties, mangosteen has the potential to be utilized in managing chronic inflammatory conditions. Here are a few examples:
Arthritis
Arthritis is a common chronic inflammatory condition that affects the joints. The anti-inflammatory effects of mangosteen can potentially alleviate the inflammation associated with arthritis, thereby reducing pain and improving joint mobility.
Allergies
Allergic reactions often involve an inflammatory response. Mangosteen’s ability to modulate immune function and inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokines can help in managing the symptoms of allergies, such as nasal congestion, sneezing, and itching.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease, including Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, involves chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. The anti-inflammatory compounds in mangosteen may help in reducing the inflammation associated with these conditions, possibly leading to symptom relief and improved gut health.
Antioxidant Properties of Mangosteen
Now that we have explored the anti-inflammatory benefits of mangosteen, let’s turn our attention to its antioxidant properties. Antioxidants are vital in protecting our bodies from the damaging effects of oxidative stress, which, as we discussed earlier, is linked to aging and various chronic diseases. Mangosteen is especially revered for its potent antioxidant capabilities, which are mainly attributed to its rich content of xanthones and other phytochemicals [6].
How Mangosteen Acts as an Antioxidant
Mangosteen’s arsenal of antioxidant compounds helps neutralize free radicals and combat oxidative stress. Let’s break down how these antioxidants function and contribute to overall health.
Neutralizing Free Radicals
Xanthones and other polyphenols in mangosteen have the ability to neutralize free radicals by donating electrons to these unstable molecules. This process prevents the free radicals from causing cellular damage, which can lead to oxidative stress and contribute to various diseases.
Boosting the Body’s Antioxidant Defenses
Mangosteen not only acts directly against free radicals but also helps bolster the body’s own antioxidant defenses. It has been suggested that compounds in mangosteen can increase the activity of antioxidant enzymes within the body, further helping to keep oxidative stress in check.
Implications for Health and Disease Prevention
The antioxidant properties of mangosteen can have a significant impact on health and may play a role in preventing various diseases.
Anti-Aging Effects
By combating oxidative stress, which is linked to the aging process, mangosteen can potentially slow down aging at the cellular level. This can manifest in better skin health, reduced wrinkles, and increased vitality.
Protection Against Chronic Diseases
Since oxidative stress is a factor in the development of many chronic diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders, mangosteen’s antioxidant properties may contribute to reducing the risk of these diseases.
Enhancing Immune Function
Antioxidants are known to support the immune system. By reducing oxidative stress, mangosteen can help maintain the integrity of immune cells, thereby potentially enhancing the body’s ability to fight off infections and diseases.
References
[1] Everything you need to know about mangosteen
[2] Purple Mangosteen
[3] Mangosteen: Purported Benefits, Side Effects & More
[4] 12 Surprising Health Benefits of Mangosteen
[5] Mangosteen
[6] Mangosteen (Garcinia mangostana) flesh supplementation attenuates biochemical and morphological changes in the liver and kidney






