
You’ve probably heard about the benefits of eating your greens, but do you know about the potent compound known as sulforaphane that’s found in cruciferous vegetables? Here we delve into the science behind sulforaphane, a phytochemical found predominantly in cruciferous vegetables like broccoli, cauliflower, kale, and Brussels sprouts. Renowned for its potential health benefits, sulforaphane is receiving increasing attention in the realms of nutrition and health research.
Contents
Introduction to Sulforaphane
Everyday foods often hold a treasure trove of health benefits, some of which are still being discovered and understood by scientists. One such food group is the cruciferous vegetable family, which is rich in a remarkable compound called sulforaphane.
Definition of Sulforaphane
Sulforaphane is a sulfur-rich compound found in substantial quantities in cruciferous vegetables. It falls under the category of phytochemicals, which are bioactive compounds in plants known for their potential health benefits. Sulforaphane is particularly notable for its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and possible anti-cancer properties.
Brief Overview of Cruciferous Vegetables
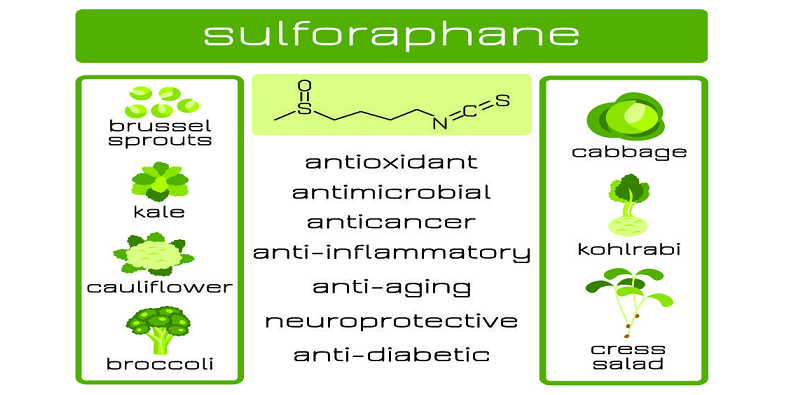
Cruciferous vegetables are a family of nutrient-dense green vegetables that include broccoli, cauliflower, kale, Brussels sprouts, and many others. Named for their cross-shaped (crucifer) flower petals, these vegetables have been recognized for their distinctive nutritional profile and potential health benefits.
The Cruciferous Vegetable Family
Diving deeper into the world of cruciferous vegetables, let’s explore this unique family of plants, their nutritional profile, and what sets them apart from other vegetable groups.
Types of Cruciferous Vegetables
Cruciferous vegetables, also known as brassicas, encompass a wide range of plants that are diverse in taste, texture, and appearance. Here are a few of the most common types:
- Broccoli: This versatile vegetable can be enjoyed raw, steamed, or roasted, and is an excellent source of vitamins C, K, and A, as well as dietary fiber.
- Cauliflower: Cauliflower has gained popularity in recent years as a low-carb alternative in various dishes. It’s also rich in vitamin C and provides a decent amount of fiber.
- Brussels Sprouts: These mini cabbages are a holiday favorite for some and are packed with vitamins K and C, along with other nutrients.
- Kale: A staple in many health-conscious diets, kale offers a wealth of nutrients, including vitamins A, K, and C, and is a good source of calcium for a leafy green.
Nutritional Profile
Cruciferous vegetables are renowned for their nutritional prowess. They are generally low in calories but high in fiber, making them a great choice for weight management. They are also rich in essential vitamins and minerals, including but not limited to, vitamins C, E, K, and A, folate, and potassium. Furthermore, they contain unique plant compounds, such as glucosinolates, which can be converted into isothiocyanates like sulforaphane, with potential health benefits [1].
How They Differ from Other Vegetables
Beyond their nutritional profile, what sets cruciferous vegetables apart is their high levels of sulfur-containing compounds called glucosinolates. When these vegetables are chopped, chewed, or cooked, an enzyme called myrosinase transforms glucosinolates into isothiocyanates, bioactive compounds that include sulforaphane. These compounds have been the subject of extensive research for their potential to benefit human health in various ways.
Understanding Sulforaphane: A Powerful Phytochemical
Now that we have a grasp of the cruciferous vegetable family, let’s zero in on one of their most potent compounds – sulforaphane.
What is a Phytochemical?
Phytochemicals, also known as phytonutrients, are natural compounds found in plant foods that, while not essential nutrients like vitamins or minerals, can have significant health-promoting properties. They are responsible for much of the color, smell, and flavor in our fruits and vegetables. More importantly, they have been linked to a reduction in the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders [2].
Discovery of Sulforaphane
Sulforaphane was first identified in 1992 by scientists at Johns Hopkins University, who were studying the potential cancer-preventive properties of cruciferous vegetables. They found that broccoli sprouts, in particular, contained high levels of this potent compound, sparking a surge of research into sulforaphane and its potential health benefits.
How Sulforaphane Works
Sulforaphane works by activating a pathway in the body known as the Nrf2 pathway. This pathway regulates the expression of antioxidant proteins that protect against oxidative damage triggered by injury and inflammation. By doing so, sulforaphane helps bolster the body’s natural defense systems, promoting overall health and well-being.
The Role of Myrosinase in Sulforaphane Production
Interestingly, sulforaphane doesn’t exist in high amounts in intact cruciferous vegetables. Instead, these vegetables contain a precursor compound called glucoraphanin. When the plant cell walls are broken through chopping, chewing, or cooking, an enzyme called myrosinase is released, converting glucoraphanin into sulforaphane. This transformation underscores the importance of how we prepare and consume these vegetables to maximize sulforaphane content [3].

Promising Health Benefits of Sulforaphane
The discovery of sulforaphane and its potential health benefits has stirred considerable interest in the scientific community. Numerous studies have explored its diverse effects on the human body, from its antioxidant properties to potential anti-cancer effects.
Antioxidant Properties
Sulforaphane is a potent antioxidant. It works by activating the Nrf2 pathway, a key regulator of antioxidant response in cells. By doing so, sulforaphane helps to neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, reducing oxidative stress and potentially lowering the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease and cancer [4].
Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Inflammation is a vital part of the body’s immune response, but when it becomes chronic, it can contribute to various health problems. Sulforaphane has been found to have anti-inflammatory properties. It inhibits the production of certain cytokines, proteins that promote inflammation, potentially aiding in the management of inflammatory diseases.
Potential Anti-Cancer Effects
One of the most exciting areas of sulforaphane research is its potential anti-cancer effects. Laboratory studies have shown that sulforaphane can inhibit the growth of cancer cells and stimulate apoptosis, or programmed cell death, in several types of cancer. While these findings are promising, more research is needed, particularly in humans, to fully understand sulforaphane’s potential as a cancer-fighting agent [5].
Neuroprotective Benefits
Emerging research suggests that sulforaphane may also have neuroprotective effects. It appears to improve brain health by reducing oxidative stress, combating inflammation, and stimulating the production of protective enzymes in the brain. These benefits could potentially play a role in preventing or slowing the progression of neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Impact on Heart Health
Sulforaphane may also contribute to heart health. Research has shown that it can help lower blood pressure, reduce inflammation and oxidative stress in the cardiovascular system, and prevent the progression of atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries.
Role in Detoxification
Another significant benefit of sulforaphane is its role in detoxification. It has been found to enhance the body’s ability to detoxify and eliminate harmful compounds, including carcinogens. By boosting the body’s detoxification pathways, sulforaphane can help protect against various forms of damage and promote overall health.

Scientific Research Supporting Sulforaphane Benefits
The potential health benefits of sulforaphane are not just theoretical; they’re supported by a growing body of scientific research. This section will explore some of the current studies on sulforaphane, their results, and limitations, as well as the future direction of research.
Current Studies on Sulforaphane
Several studies have sought to investigate the effects of sulforaphane on human health. For instance, a study published in “Cancer Prevention Research” in 2015 found that a daily dose of sulforaphane-rich broccoli sprout extract over several months reduced the rate of tumor progression in men with early-stage prostate cancer [6].
In another study published in the “International Journal of Epidemiology,” researchers found that a higher intake of cruciferous vegetables was associated with a lower risk of heart disease, potentially due to compounds like sulforaphane.
Neurodegenerative diseases have also been a focus of sulforaphane research. A study published in “Molecular Neurobiology” in 2017 suggested that sulforaphane might help protect the brain from damage and improve cognitive function in the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease.
Results and Interpretation
While these studies and others like them are promising, it’s important to interpret the results with caution. Many studies have been conducted in lab settings or on animals, and results may not always translate directly to humans. Even in human studies, many factors can influence the results, such as the participants’ overall diet and lifestyle, the amount of sulforaphane consumed, and the method of consumption.
Limitations and Future Research
Current research on sulforaphane is still limited, and more extensive, long-term studies in humans are needed to confirm its potential health benefits. The optimal dosage of sulforaphane, the best ways to consume it, and its long-term effects are all areas that need further exploration.
References
[1] Sulforaphane benefits: How broccoli and Brussels sprouts may help reduce your cancer risk
[2] Sulforaphane: How to Gain Its Benefits Both Raw and Cooked
[3] What is Sulforaphane — And Why Is It so Good for You?
[4] Lesson 28: Sulforaphane
[5] Potential health benefits of sulforaphane: A review of the experimental, clinical and epidemiological evidences and underlying mechanisms
[6] Current potential health benefits of sulforaphane






