
Astaxanthin is a remarkable compound often referred to as nature’s most potent antioxidant. Antioxidants play a critical role in our overall health and well-being, acting as our body’s defense force against free radicals, unstable molecules that can cause damage to our cells. Among the diverse range of antioxidants known to us, Astaxanthin stands out for its extraordinary potency and the array of health benefits it offers. Astaxanthin is a naturally occurring compound found in certain algae and seafood. Here we examine exactly what makes it so special.
Contents
Understanding Astaxanthin
Before we delve into the multitude of benefits that Astaxanthin offers, it is crucial to first understand what Astaxanthin is, its natural sources, and how it works on a molecular level. This will provide a strong foundation for our discussion on why Astaxanthin is such a powerful antioxidant.
What is Astaxanthin?
Astaxanthin is a carotenoid, a naturally occurring pigment that gives many fruits and vegetables their vibrant colors. It is particularly responsible for the reddish-pink hue found in salmon, shrimp, and some crustaceans. But Astaxanthin is more than just a pigment. It is a potent antioxidant, recognized for its ability to neutralize free radicals and reduce oxidative stress in the body.
Natural Sources of Astaxanthin
Astaxanthin is primarily produced by microalgae and yeast as a defense mechanism against harsh environmental conditions, such as lack of nutrients or excessive sunlight. When predators like shrimp or krill consume these algae, they too gain the red pigment, and this process continues up the food chain. Therefore, the highest concentrations of Astaxanthin are found in marine life, particularly in wild Pacific salmon, krill, red trout, shrimp, crawfish, and crustaceans.
While Astaxanthin can also be found in certain birds, such as flamingos and quail, that consume a diet rich in carotenoids, the most bioavailable sources for human consumption remain seafood and microalgae-based supplements.
The Chemistry of Astaxanthin: How It Works
To fully appreciate the power of Astaxanthin, it’s important to understand how it functions. Astaxanthin, like all antioxidants, works by neutralizing free radicals — unstable atoms that can damage cells, causing illness and aging. Free radicals are produced naturally in our bodies through metabolic processes, but they can also come from external sources, such as pollution, tobacco smoke, and UV rays [1].
Astaxanthin is uniquely structured to permeate cell membranes and extend across them. This positioning allows Astaxanthin to trap and quench free radicals in both the inner and outer cell layers, providing comprehensive protection. Moreover, Astaxanthin never becomes a pro-oxidant, meaning it does not induce oxidation in other molecules or become a free radical itself, unlike some other antioxidants.
Understanding this chemistry underscores the potency of Astaxanthin and sets the stage for our exploration of the numerous health benefits it offers, which we will discuss in the following sections.

The Potency of Astaxanthin as an Antioxidant
Now that we have a fundamental understanding of Astaxanthin, let’s dive deeper into its potency as an antioxidant. In this section, we will compare Astaxanthin with other well-known antioxidants and shed light on the scientific evidence that underscores its superior antioxidant capacity.
Comparison of Astaxanthin with Other Antioxidants
Astaxanthin is often hailed as the “king of the carotenoids” due to its remarkable antioxidant power. To put things in perspective, it’s worth comparing Astaxanthin with other well-known antioxidants.
According to various research studies, Astaxanthin is 6,000 times stronger than vitamin C, 800 times stronger than CoQ10, 550 times stronger than green tea catechins, and 75 times stronger than alpha-lipoic acid in terms of antioxidant activity. It even surpasses other carotenoids like beta-carotene and lycopene. This potency is primarily attributed to Astaxanthin’s unique molecular structure, which allows it to quench free radicals more effectively and across various layers of the cell membrane [2].
Scientific Evidence Supporting Astaxanthin’s Potency
Several scientific studies have been conducted to understand the antioxidant potency of Astaxanthin. One such study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry showed that Astaxanthin demonstrated the highest antioxidant activity against free radicals among the carotenoids tested.
Another study, published in the Carotenoid Science journal, demonstrated that Astaxanthin was particularly effective in combatting a specific type of oxidative damage known as singlet oxygen quenching. The study concluded that Astaxanthin was approximately 800 times more effective in this regard than CoQ10 and 6000 times more than Vitamin C [3].
These studies, among others, provide robust scientific evidence that supports Astaxanthin’s standing as a superior antioxidant. However, the real power of Astaxanthin comes to light when we consider the numerous health benefits it offers, which we will explore in the next section.
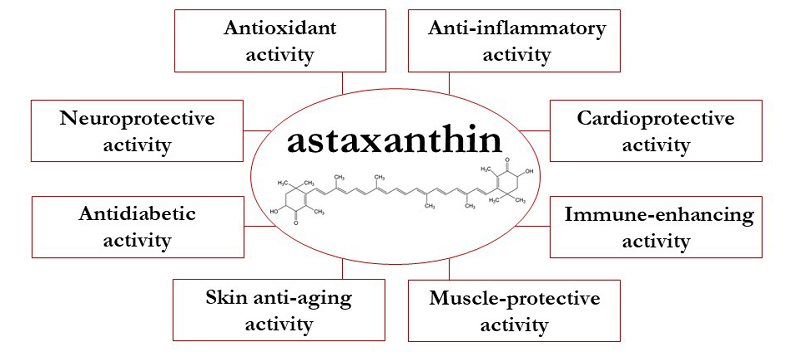
Health Benefits of Astaxanthin
Having established Astaxanthin’s potency as an antioxidant, it’s time to explore the multitude of health benefits associated with it. From promoting skin health to enhancing cardiovascular well-being, Astaxanthin’s impact on human health is profound and multi-faceted. Let’s delve into some of the significant benefits that scientific research has brought to light.
Skin Health and Anti-Aging Benefits
Astaxanthin’s potent antioxidant activity provides significant benefits for skin health and aging. It helps protect the skin from damage caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays, one of the primary causes of skin aging. Studies have shown that Astaxanthin can improve skin elasticity, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and increase skin moisture levels.
Moreover, Astaxanthin’s anti-inflammatory properties can help reduce redness and inflammation associated with various skin conditions, including rosacea and dermatitis. As such, Astaxanthin is often found in skincare products, but it can also benefit the skin when ingested through diet or supplements.
Eye and Brain Health
Astaxanthin’s unique molecular structure allows it to cross the blood-brain and blood-retinal barriers, which most other antioxidants can’t penetrate. This means Astaxanthin can deliver antioxidant protection directly to the eyes and brain, reducing oxidative stress and inflammation that could lead to conditions like age-related macular degeneration, glaucoma, cataracts, and neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s [4].
Several studies have shown that regular consumption of Astaxanthin can improve visual acuity and eye health, while also promoting cognitive function and brain health.
Cardiovascular Health
Astaxanthin’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties can significantly benefit cardiovascular health. By reducing oxidative stress and inflammation in the blood vessels, Astaxanthin can help prevent the formation of plaque, which leads to atherosclerosis or hardening of the arteries. Furthermore, research has indicated that Astaxanthin can improve lipid profiles by increasing ‘good’ HDL cholesterol and decreasing ‘bad’ LDL cholesterol, reducing the risk of heart disease.
Joint and Muscular Health
Astaxanthin’s potent anti-inflammatory properties make it a powerful natural remedy for joint and muscle health. It can help alleviate symptoms of conditions such as arthritis and carpal tunnel syndrome. Moreover, Astaxanthin has been found to improve muscle endurance and recovery, making it particularly beneficial for athletes and individuals with physically demanding routines.
Immune System Boost
Astaxanthin has been shown to enhance the immune response, increase the production of antibodies, and decrease DNA damage, thus helping the body resist infections and diseases. Its anti-inflammatory properties can also help modulate the immune system, preventing overactive immune responses that can lead to autoimmune conditions [5].
Potential Anti-Cancer Properties
Several studies have suggested that Astaxanthin may have potential anti-cancer properties. It has been found to inhibit the growth of various types of cancer cells in laboratory settings and reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, which are key contributors to cancer development. However, more research is needed to fully understand Astaxanthin’s potential role in cancer prevention and treatment.

Astaxanthin in the Diet
Having explored the multitude of health benefits Astaxanthin offers, you might be wondering how to incorporate this potent antioxidant into your diet. The good news is that Astaxanthin can be found in several dietary sources, primarily from marine life. However, the concentration of Astaxanthin in these foods may vary, and its absorption can be influenced by several factors.
Foods Rich in Astaxanthin
As mentioned earlier, Astaxanthin is found in the highest concentrations in certain types of seafood, thanks to the marine food chain. Wild Pacific salmon, especially sockeye salmon, is one of the richest sources of dietary Astaxanthin. Other seafood sources include shrimp, lobster, crab, and krill. If you’re a seafood lover, incorporating these into your diet can help you benefit from Astaxanthin.
However, it’s important to note that the concentration of Astaxanthin in these foods is relatively low compared to what you may find in supplements. For example, a serving of wild salmon contains about 3.6 mg of Astaxanthin, while a typical Astaxanthin supplement can provide anywhere from 4 to 12 mg per serving.
How to Incorporate Astaxanthin into Your Diet
While consuming Astaxanthin-rich foods is a good starting point, it may not be sufficient to obtain its full health benefits due to the relatively low concentration of Astaxanthin in these foods. This is where Astaxanthin supplements can come into play.
Astaxanthin is fat-soluble, meaning it needs to be consumed with a source of fat for optimal absorption. Whether you’re eating Astaxanthin-rich foods or taking a supplement, pairing it with a healthy source of fat like avocados or nuts can enhance its absorption.
Astaxanthin Supplements
Given the relatively low concentrations of Astaxanthin in food sources, many people turn to supplements to ensure they are getting an adequate amount of this potent antioxidant. However, not all supplements are created equal. It’s important to understand what to look for when choosing an Astaxanthin supplement to ensure you’re getting a high-quality product that your body can effectively use.
Understanding Astaxanthin Supplements
Astaxanthin supplements come in various forms, including softgels, capsules, and liquid drops. They are primarily derived from two sources: the microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis, the richest natural source of Astaxanthin, or synthetically produced in a lab.
While synthetic Astaxanthin is cheaper to produce and often found in animal feed, it’s not as effective or beneficial as natural Astaxanthin for human consumption. Natural Astaxanthin from microalgae has been found to be over 20 times stronger in free radical scavenging and 50 times stronger in singlet oxygen quenching than the synthetic version. Therefore, it’s crucial to choose a supplement that contains natural Astaxanthin.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Astaxanthin Supplement
When choosing an Astaxanthin supplement, the first thing to check is that it contains natural Astaxanthin derived from microalgae. Next, look at the dosage. Most studies showing health benefits have used doses between 4 to 12 mg per day.
Other factors to consider include:
- Purity: The supplement should be free from harmful contaminants.
- Additives: Ideally, the supplement should not contain unnecessary additives or fillers.
- Brand reputation: Choose a supplement from a reputable brand known for its quality control and transparency.
- Carrier oil: Since Astaxanthin is fat-soluble, some supplements include a carrier oil (like olive oil or coconut oil) to enhance absorption.
Recommended Dosage and Safety Information
The recommended dosage of Astaxanthin varies depending on the specific health goal, but generally, a daily dose of 4-12 mg is suggested for overall health and wellness. As with any supplement, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare provider before starting.
Astaxanthin is considered safe with few reported side effects. However, high doses might cause a slight orange tint to the skin, similar to the effect of eating large amounts of carrots. As a natural substance found in common foods, Astaxanthin has an excellent safety profile.
References
[1] Astaxanthin: focus on one of the most potent natural antioxidants
[2] Surface-mediated high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of astaxanthin
[3] Antioxidant Activities of Astaxanthin and Related Carotenoids
[4] Natural Astaxanthin Is a Green Antioxidant Able to Counteract Lipid Peroxidation and Ferroptotic Cell Death
[5] Antioxidant effects of astaxanthin in various diseases — a review






