
What is the secret to happiness? How can we cultivate positivity in our lives? These age-old questions have sparked interest and debate among philosophers, researchers, and seekers of wisdom throughout history. The pursuit of happiness is a universal human endeavor, and science has provided fascinating insights into this quest. Here we look into the multi-faceted nature of happiness, examining it from biological, psychological, and social perspectives.
Contents
Introduction to the Science of Happiness
Throughout history, humans have been on a relentless quest for happiness. It’s a universal pursuit, spanning across ages, cultures, and societies. But what is happiness, exactly? And is it truly achievable? With the advancement of science and technology, we now have a clearer understanding of what happiness means and how it can be cultivated. The science of happiness, an exciting and emerging field, combines various aspects of biology, psychology, and social sciences to offer a comprehensive view of happiness.
Definition of Happiness
At its most fundamental, happiness is a state of well-being that encompasses living a good life, one with a sense of deep satisfaction and joy. It’s more than a transient state of pleasure; rather, it involves a durable sense of contentment. However, it’s important to note that the definition of happiness can vary greatly between different cultures and individuals. What might bring happiness to one person might not have the same effect on another, emphasizing the subjectivity of this concept.
Brief Overview of the Role of Science in Studying Happiness
Science has long been interested in the study of happiness, contributing significantly to our understanding of this complex emotion. From the neurobiological processes that occur in our brains to the psychological and social factors that influence our perception of happiness, scientific research has provided valuable insights. The science of happiness, also closely associated with positive psychology, uses empirical methods to explore ways to foster well-being and flourishing in individuals and communities.
Importance of Happiness in Our Lives
Why is happiness so important? In addition to being a desirable state, research shows that happiness is associated with numerous benefits. Happier individuals tend to have better physical and mental health, enjoy stronger relationships, and even live longer. Furthermore, happiness can improve productivity and creativity, indicating its role not just in personal lives but also in professional domains. Thus, understanding and cultivating happiness can greatly enrich our lives, making the pursuit of happiness a worthy endeavor.

The Biological Basis of Happiness
While happiness might seem intangible, it’s deeply rooted in our biology. As we explore the biological basis of happiness, we will delve into the complex interplay between our brains, genetics, and physical health in our experience of happiness. Understanding this connection can empower us to take concrete steps towards enhancing our well-being.
The Brain and Happiness
Our brain, often termed the command center of the human body, plays a pivotal role in our emotional experiences, including happiness. It is where various neurotransmitters and neural pathways work together to create the feelings and emotions we associate with happiness.
The Role of Neurotransmitters
Neurotransmitters are chemicals in our brain that transmit signals between nerve cells, affecting various bodily functions, including mood regulation. Three key neurotransmitters are involved in promoting feelings of happiness and well-being [1].
- Serotonin: Often dubbed the ‘happy chemical’, serotonin helps regulate mood, appetite, sleep, and even social behavior. Insufficient levels of serotonin are linked to depression. Many antidepressants work by increasing serotonin levels in the brain.
- Dopamine: Dopamine is associated with the brain’s reward system. It is released when we experience something pleasurable, driving motivation and reinforcing the action that led to the pleasure. It is thus often linked to the joy we feel upon achieving a goal.
- Endorphins: Endorphins act as natural painkillers and create feelings of euphoria. They’re often released during exercise, which is why we may feel a ‘runner’s high’ after a rigorous workout.
The Reward System and Happiness
Our brain’s reward system, primarily driven by dopamine, is directly linked to our experience of pleasure and happiness. When we engage in activities we enjoy, whether it’s eating a favorite meal or spending time with loved ones, our reward system is activated, leading to the release of dopamine and generating feelings of happiness and satisfaction.
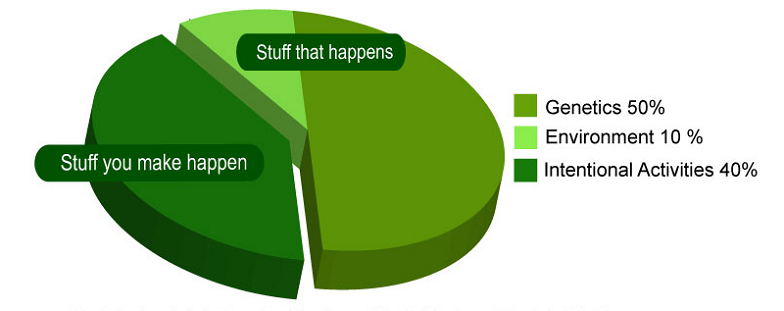
The Role of Genetics in Happiness
Research suggests that genetics also play a part in our happiness. Twin and family studies have found a significant heritable component of happiness, indicating that our capacity for happiness is partly predetermined by our genes. However, it’s important to note that while genetics set the stage, our environment and personal choices also significantly impact our happiness levels. In other words, even if we’re genetically predisposed towards lower happiness, we can still take steps to improve our well-being [2].
The Influence of Physical Health on Happiness
Our physical health significantly affects our emotional state. Regular physical activity stimulates the production of endorphins, boosting mood and energy levels. A balanced, nutritious diet can influence the production of neurotransmitters, and adequate sleep is essential for regulating mood and promoting overall well-being. Conversely, chronic illness or poor health can lead to decreased happiness, highlighting the importance of maintaining good health to support emotional well-being.
Psychological Perspectives on Happiness
Our psychological make-up and mindset play a significant role in our pursuit of happiness. While our biology lays the groundwork, it’s our psychology that often shapes how we interpret our life experiences and influences our happiness.
Positive Psychology and Happiness
Positive psychology is a branch of psychology that focuses on the positive aspects of human life, including happiness, optimism, and personal growth. Instead of focusing solely on mental illness, it emphasizes the importance of building strengths and virtues that help individuals thrive.
The Work of Martin Seligman
Martin Seligman, a pioneer in the field of positive psychology, has contributed significantly to our understanding of happiness. He proposed the concept of ‘authentic happiness,’ which includes three components: positive emotions (the pleasurable life), engagement (the engaged life), and meaning (the meaningful life). Seligman argued that true, lasting happiness comes from a combination of these three elements [3].
The PERMA Model
Seligman later expanded the concept of authentic happiness into the PERMA model, a comprehensive framework for understanding well-being. PERMA stands for Positive emotions, Engagement, Relationships, Meaning, and Accomplishment. According to Seligman, these five elements are essential for human flourishing and happiness.
The Role of Mindset in Happiness
Your mindset, the way you think about yourself and the world around you, plays a critical role in your happiness. Cultivating a positive mindset can significantly enhance your sense of well-being. This includes practices such as positive self-talk, embracing challenges as opportunities for growth (growth mindset), and adopting an attitude of gratitude. The way we interpret our experiences can make a considerable difference in our overall happiness.
The Importance of Emotional Intelligence
Emotional Intelligence (EI), the ability to identify, understand, and manage emotions, is another significant psychological factor in happiness. High EI is associated with better stress management, healthier relationships, and, importantly, higher levels of happiness.
By learning to navigate our emotions effectively, we can respond to life’s ups and downs in ways that foster well-being and happiness [4].
Understanding these psychological perspectives on happiness gives us insight into how our thoughts, attitudes, and emotional skills can shape our happiness. They also provide practical strategies that we can implement in our lives to enhance our well-being.

The Social Aspect of Happiness
Happiness isn’t just an individual pursuit; it is deeply intertwined with our social relationships and the communities we belong to. The people we surround ourselves with, the quality of our interpersonal relationships, and the societal norms and cultures we live in significantly shape our happiness.
The Role of Relationships and Social Connections
Human beings are inherently social creatures. The relationships we form—with family, friends, colleagues, and even with our broader community—can have a profound impact on our happiness. Studies have consistently found that individuals who have strong, positive social relationships tend to be happier [5].
These relationships provide support, create a sense of belonging, and offer opportunities for positive experiences. They can also help us during challenging times, offering emotional support and practical help. Thus, investing in our relationships is a valuable strategy for enhancing happiness.
Community, Belonging, and Happiness
Feeling a sense of belonging to a community can significantly contribute to our happiness. This can be a geographical community, like a neighborhood or town, or a community based on shared interests or experiences. Being part of a community offers a sense of identity and provides opportunities for social connections, support, and shared experiences, all of which can enhance happiness.
Volunteering and contributing to one’s community can also boost happiness by providing a sense of purpose and fulfillment. Acts of kindness and cooperation stimulate the release of endorphins, contributing to a state of euphoria known as a ‘helper’s high.’
The Influence of Culture and Society on Happiness
Cultural and societal norms can also shape our happiness. Different cultures have different definitions and standards of happiness, which can influence how individuals pursue and experience happiness. For example, in Western societies, happiness is often linked with personal achievements and individualism, while Eastern cultures may associate happiness more with social harmony and collective well-being.
Furthermore, societal factors such as economic stability, political freedom, and access to healthcare and education can also influence happiness at a broader level. Studies have shown that societies that meet their citizens’ basic needs and provide a supportive social environment tend to have happier citizens.
Recognizing the social aspect of happiness reminds us that our well-being is linked to others and to the world around us. It also underlines the importance of fostering positive relationships and communities in our pursuit of happiness.
Practical Strategies for Cultivating Positivity and Happiness
Now that we’ve explored the biology, psychology, and sociology of happiness, it’s time to look at some practical strategies to cultivate positivity and happiness in our daily lives. These techniques draw from the insights we’ve learned, offering concrete steps to enhance our well-being.
Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness involves being fully present in the moment, aware of our thoughts, feelings, and sensations without judgment. Practicing mindfulness can help us savor positive experiences, manage stress, and respond rather than react to challenging situations, all of which can enhance happiness. One way to cultivate mindfulness is through meditation, a practice that has been found to promote relaxation, reduce stress, and increase happiness [6].
Cultivating Gratitude
Gratitude is a powerful emotion that can boost happiness. Taking time to appreciate the good in our lives, big or small, shifts our focus from what’s wrong to what’s right, promoting positivity. Try keeping a gratitude journal, writing down three things you’re thankful for each day. This practice can increase optimism, improve sleep, and enhance overall well-being.
Engaging in Physical Activity
As we’ve learned, physical health significantly influences our happiness. Regular physical activity stimulates the production of endorphins, creating feelings of happiness and euphoria. Whether it’s jogging, yoga, or dancing, find an activity you enjoy and make it a part of your routine.
Investing in Relationships
Given the strong link between social connections and happiness, investing time and energy in our relationships is key. This could involve spending quality time with loved ones, expressing appreciation, or offering support during difficult times. Building strong, positive relationships can significantly enhance our happiness.
Seeking Professional Help When Needed
Lastly, it’s important to remember that if you’re struggling with persistent unhappiness or mental health issues, it’s okay to seek professional help. Therapists and counselors can provide support, teach valuable coping strategies, and offer a safe space to explore your feelings.
References
[1] The Science of Happiness: Psychology explores humans at their best.
[2] The Science of Happiness in Positive Psychology 101
[3] The Science of Happiness
[4] The Neuroscience of Happiness and Pleasure
[5] 5 Ways To Increase Your Happiness, According to Science
[6] The Science Behind the Smile






